Recently, the underwater hidden pipe side-scan sonar detection mission in a certain water area of Xuzhou was successfully concluded. The unmanned vessel, relying on side-scan sonar technology and an intelligent navigation system, successfully completed the hidden pipe inspection and data collection in the target water area, providing precise technical support for local water environment governance.
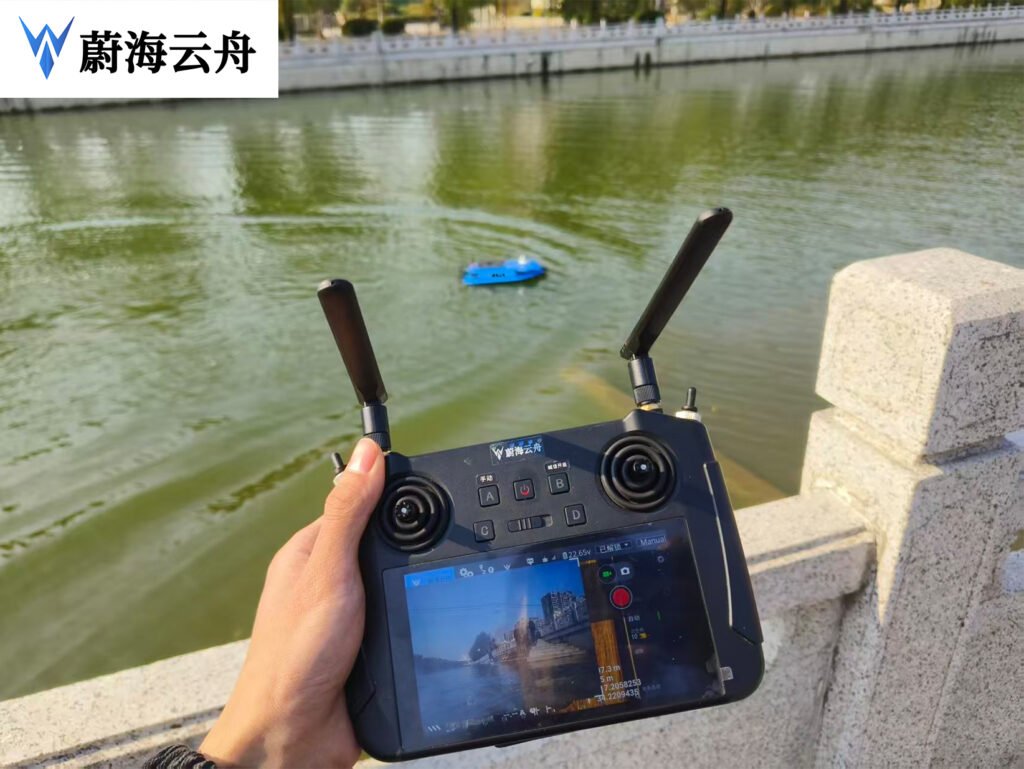

Task Background: The “Pain Points” of Hidden Pipe Inspection and the “Breakthrough” of Unmanned Ships
Underwater concealed pipes are the “hidden source” of water environmental pollution. Traditional manual investigation faces problems such as complex water areas, high risks and low efficiency. The water area detected in Xuzhou this time is deep and the water quality is turbid. Manual underwater operation is not only dangerous but also difficult to accurately locate the position of the concealed pipes. To this end, the local area has introduced unmanned ships equipped with side-scan sonar to break through the technical bottleneck of hidden pipe inspection in an “unmanned and intelligent” way.
Technical core: “Precise Detection combination” of side-scan sonar and unmanned ships
The unmanned vessel adopted in this mission is equipped with high-resolution side-scan sonar, and its core technical advantages are significant:
Sonar imaging is precise: By adopting a 100kHz bandwidth signal and variable aperture dynamic focusing technology, it breaks through the problem of “near-field blurring” in traditional sonar, achieving high-definition imaging of underwater terrain and objects, with the contours of dark tubes clearly distinguishable.
Autonomous operation of unmanned vessels: By planning routes through GPS and Beidou navigation, unmanned vessels automatically cruise and cover the target waters, avoiding errors caused by manual operation.
Real-time data transmission: Sonar detection data and underwater images are synchronously transmitted to the shore-based control terminal. Staff can analyze the location of suspected hidden pipes in real time without waiting on site.
Task outcome: Efficiently identify hidden pipes, providing solid evidence for governance

In this exploration, the unmanned vessel completed a full coverage scan of a 5-kilometer river section in just 2 hours, which is more than 10 times more efficient than the traditional manual method.
Precise location of concealed pipes: The side-scan sonar clearly captured the acoustic images of suspected concealed pipes underwater. Combined with AI interpretation technology, the specific locations of two concealed sewage pipes were identified (with an error controlled within 0.3 meters).
Data-linked traceability: The unmanned vessel simultaneously collected water quality data (such as ammonia nitrogen concentration) around the concealed pipe, forming an evidence chain of “concealed pipe location + pollution data” with the sonar detection results, providing a reliable basis for subsequent law enforcement and governance.
Zero safety risk: The entire process is unmanned, avoiding the health risks of personnel entering polluted waters. At the same time, it maintains stable navigation in complex water flow environments, ensuring the continuity of the detection mission.
Value and Significance: The “Xuzhou Practice” of Empowering Water Environment Governance with Technology
This unmanned vessel concealed pipe detection mission is an important attempt by Xuzhou to promote intelligent and precise water environment governance.

From “human sea tactics” to “technological breakthroughs”, the combination of unmanned ships and side-scan sonar has significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of hidden pipe inspection.
It provided data support for the subsequent rectification of sewage outlets and water quality restoration, helping the local area achieve an integrated water environment management of “source, network, factory and river”.
It also provided a replicable “Xuzhou experience” for the investigation of hidden pollution sources in other cities, demonstrating the application potential of unmanned vessel technology in the field of ecological and environmental protection.
With the popularization of intelligent equipment such as unmanned ships, water environment governance is shifting from “passive response” to “active prevention and control”, using the power of technology to safeguard clear waters and flowing streams.
